

For example, you can use it to determine if and to what extent experience or gender impacts salaries. Typically, you need regression to answer whether and how some phenomenon influences the other or how several variables are related. If there are two or more independent variables, then they can be represented as the vector 𝐱 = (𝑥₁, …, 𝑥ᵣ), where 𝑟 is the number of inputs. It’s a common practice to denote the outputs with 𝑦 and the inputs with 𝑥. The inputs, however, can be continuous, discrete, or even categorical data such as gender, nationality, or brand. Regression problems usually have one continuous and unbounded dependent variable. The independent features are called the independent variables, inputs, regressors, or predictors. The dependent features are called the dependent variables, outputs, or responses. In other words, you need to find a function that maps some features or variables to others sufficiently well. Following the assumption that at least one of the features depends on the others, you try to establish a relation among them. Each observation has two or more features. Generally, in regression analysis, you consider some phenomenon of interest and have a number of observations. Similarly, you can try to establish the mathematical dependence of housing prices on area, number of bedrooms, distance to the city center, and so on.

The presumption is that the experience, education, role, and city are the independent features, while the salary depends on them. This is a regression problem where data related to each employee represents one observation. For example, you can observe several employees of some company and try to understand how their salaries depend on their features, such as experience, education level, role, city of employment, and so on. Regression searches for relationships among variables.
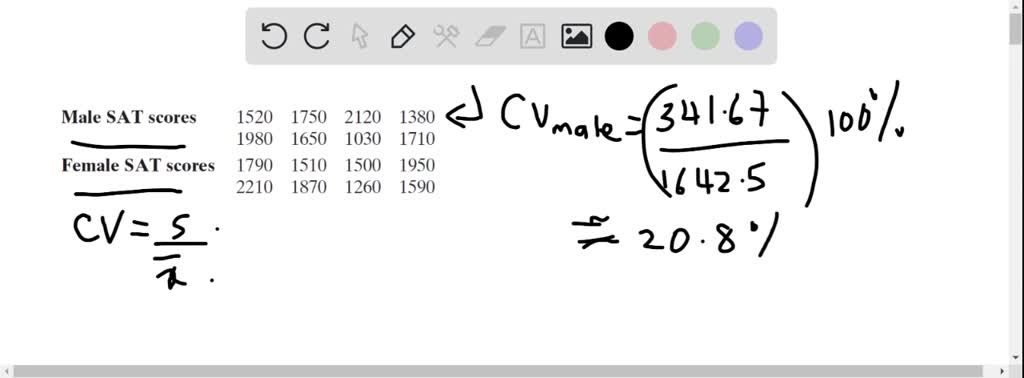
#Coefficient of variation easycalculator how to
Watch Now This tutorial has a related video course created by the Real Python team.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
